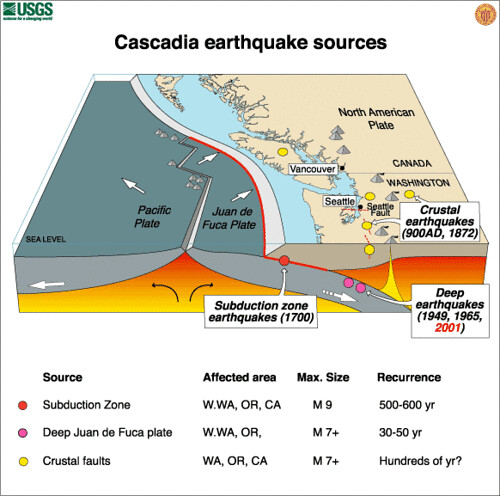
Sand blows formed after the 2012 Emilia earthquake in Italy, indicating
4.6 (668) · $ 13.99 · In stock
Download scientific diagram | Sand blows formed after the 2012 Emilia earthquake in Italy, indicating pore-water escape and liquefaction/luidization, which must have resulted in the formation of SSDS of a buried layer, which consequently should be considered as a seismite (from Emergeo Working Group, 2012). from publication: Restrictions to the application of ‘diagnostic’ criteria for recognizing ancient seismites | Soft-sediment deformation structures induced by seismic liquefaction and/or fluidization receive much attention in sedimentological, structural and palaeoseismic studies. The direct record of larger earthquakes is restricted to instrumental and historical data; the | Congenital Abnormalities, Seismics and Restriction | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Interplay of Holocene surface faulting and climate in the Central

Failure of industrial structures induced by the Emilia (Italy

Geosciences, Free Full-Text

Liquefaction source layer for sand blows induced by the 2016

Sand blows formed after the 2012 Emilia earthquake in Italy, indicating

Sand liquefaction during the 2021 M 7.4 Maduo earthquake, China

PDF) The survey and mapping of sand-boil landforms related to the
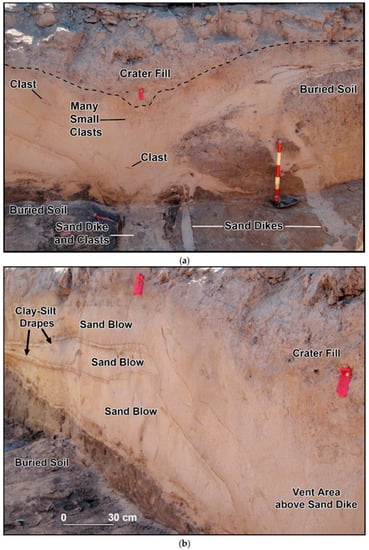
Geosciences, Free Full-Text

Area of the Emilia 2012 earthquake sequence. (a), (b), (c) main

The influence of sedimentary architecture on the formation of

Earthquake down time Davide Barranca — Photoshop, etc.

Interplay of Holocene surface faulting and climate in the Central

Restrictions to the application of 'diagnostic' criteria for recognizing ancient seismites - ScienceDirect

Liquefied sites of the 2012 Emilia earthquake: a comprehensive

Liquefaction, New Madrid Seismic Fault region sandy soil