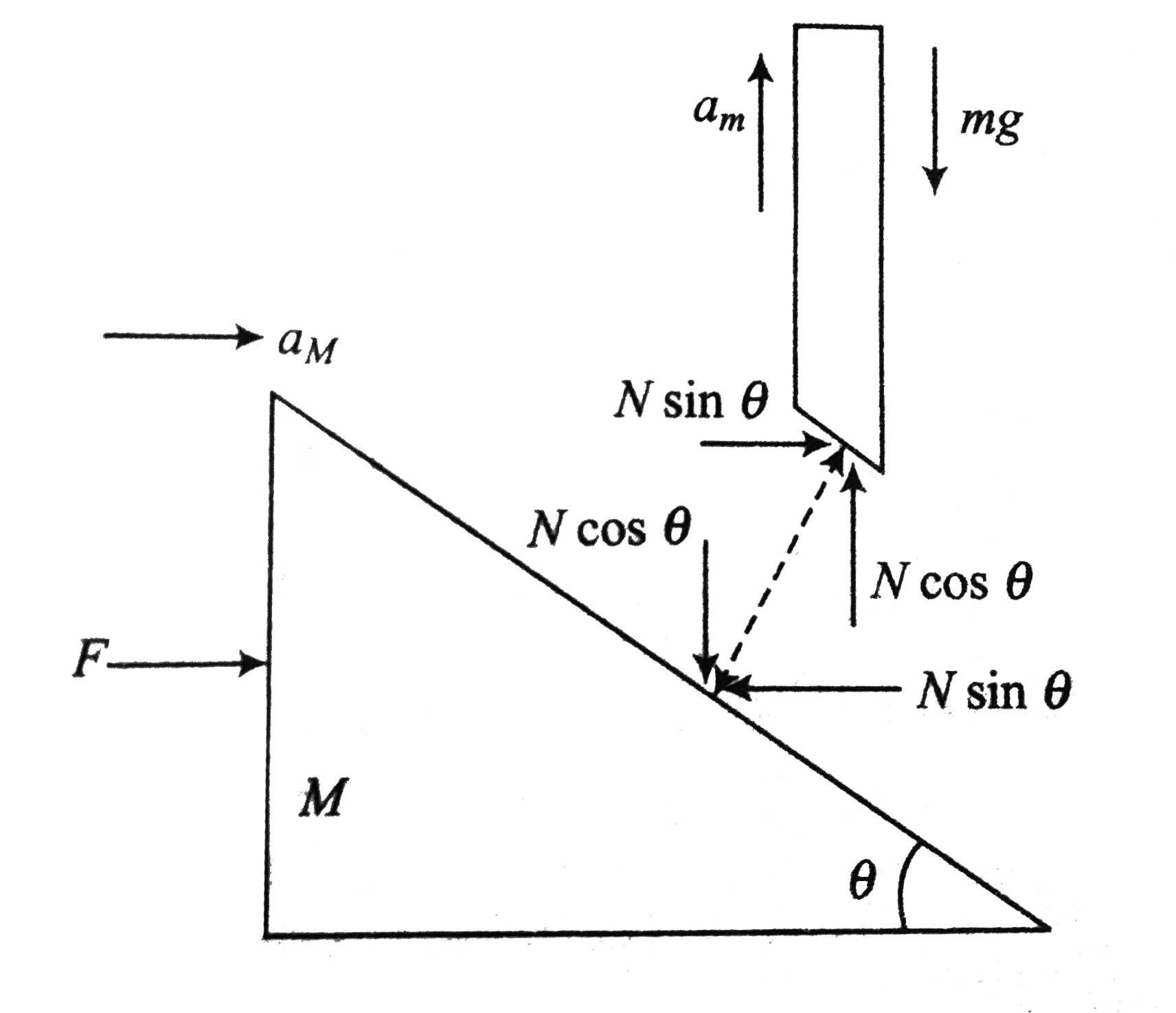
A rod of mass m is supported on a wedge of mass M. Shown in Fig
4.7 (505) · $ 25.50 · In stock
Click here:point_up_2:to get an answer to your question :writing_hand:a rod of mass m is supported on a wedge of mass m shown in
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ✍️ A rod of mass m is supported on a wedge of mass M- Shown in Fig- 6-159- Find the accelerations of rod a and wedge A in the arrangement- The friction between all contact surface is negligible-
The rod is constrained to move in the vertical direction -with the help of the guides- and the wedge will move along the surface in the horizontal direction- Initially- the system is held at rest-Constraint relation - Approach 1Let the acceleration of m w-r-t- ground be a vertically downwards and acceleration of M w-r-t- ground be A horizontally towards right-The motion of the system is constrained by the fact that the -apos-bottom face of the rod must always be in contact with the inclined plane-quot- If in time t- X is the displacement of the wedge and x is the displacement of the rod- then the constraint demands thatFrom Fig- we have xX-tan-x3B1-x2234-xA0- -xA0- x-Xtan-x3B1-i-Here -x3B1- remains constant-Differentiating -i- w-r-t- t twice- we get-xA0- -xA0- -xA0- -xA0-d2xdt2-d2Xdt2-tan-x3B1-xA0- -xA0- -xA0- -tan-x3B1-constant-Hence- a-Atan-x3B1-Approach 2 -xA0-xA0-The fact that the rod -or a particle on the wedge- and the wedge must not lose contact is usually called wedge constraints- For this- the component of the acceleration of the rod perpendicular to the wedge plane- component of acceleration of the wedge perpendicular to wedge plane-xA0- acos-x3B1-Asin-x3B1-x21D2-a-Atan-x3B1-The force acting on the rod are-x2219- The weight mg- vertically downwards-x2219- The normal force N- normal to the bottom surface of the rod-x2219- The force -Fguide- exerted by the guide to nullify the horizontal component of N as for the rod ahorizontal-0-Motion in vertical direction-xA0- -xA0-mg-x2212-Ncos-x3B1-ma-ii-and the forces acting on the wedge are-x2219- The weight- Mg-x2219- reaction of N acting on the rod-x2219- N1- normal force by the surfaceThe force equations are-xA0-xA0- -xA0- -xA0-N1-x2212-Mg-x2212-Ncos-x3B1-0-iii-and-xA0- -xA0- Nsin-x3B1-MA-v-Solving the above equations for a and A- we get-xA0- -xA0-a-mgtan-x3B1-mtan-x3B1-Mcos-x3B1- and A-mgmtan-x3B1-Mcos-x3B1

A rod of mass m is supported on a wedge of mass M shown in fig. Find t

A block of mass m lies on wedge of mass Mas shown in figure. Find
A rod of mass m and length l is kept on a smooth wedge of mass M

Find the acceleration of the block B as shown in figure- 1.95 (a

the surface of the wedge of masih mesturningal the In the

A rod of length l and mass m rotates about end A in vertical plane
Classical Mechanics - Statics - Mass and overhang

Find the acceleration of the block B as shown in figure- 1.95 (a
A vertical rod of mass m is kept on a wedge of mass M. If a horizontal












